What do you need to study for neurology?
Research Methodologies for Neurology
The field of neurology relies heavily on various research methodologies to advance understanding and treatment of neurological disorders. Qualitative and quantitative research methods play vital roles in exploring the complexities of brain function and dysfunction. Observational studies can highlight real-world patient experiences, while controlled laboratory experiments offer insights into underlying mechanisms of diseases. These methodologies work together, providing rich data that informs clinical practice and guides future research directions.
Increasingly, neurology research incorporates innovative approaches, such as big data analytics and machine learning. These techniques allow for the analysis of vast datasets, uncovering patterns and correlations that traditional methods might miss. Such advancements not only enhance diagnostic accuracy but also facilitate personalized treatment strategies, tailoring interventions based on individual patient profiles. Collaboration among neurologists, data scientists, and other specialists is crucial for maximizing the potential of these methodologies.
Understanding Clinical Trials and Studies
Clinical trials and studies form the backbone of evidence-based practice in neurology. Researchers design these studies to evaluate the efficacy of new treatments, understand disease mechanisms, and explore the effects of various interventions on patient outcomes. The process typically moves through several phases, starting with small-scale trials focusing on safety before expanding to larger groups that assess effectiveness. Patient recruitment, informed consent, and ethical considerations play crucial roles in ensuring that trials are not only scientifically robust but also ethically sound.
Data collection and analysis are vital components of clinical studies. Researchers track specific outcomes related to neurological conditions, which might include cognitive function, symptom progression, or quality of life among participants. Advanced statistical methods help analyze the results, leading to conclusions that can guide clinical practices and inform guidelines. The integration of clinical trial findings into everyday medical practice is essential, fostering improvements in treatment protocols and ultimately benefiting patients facing neurological challenges.
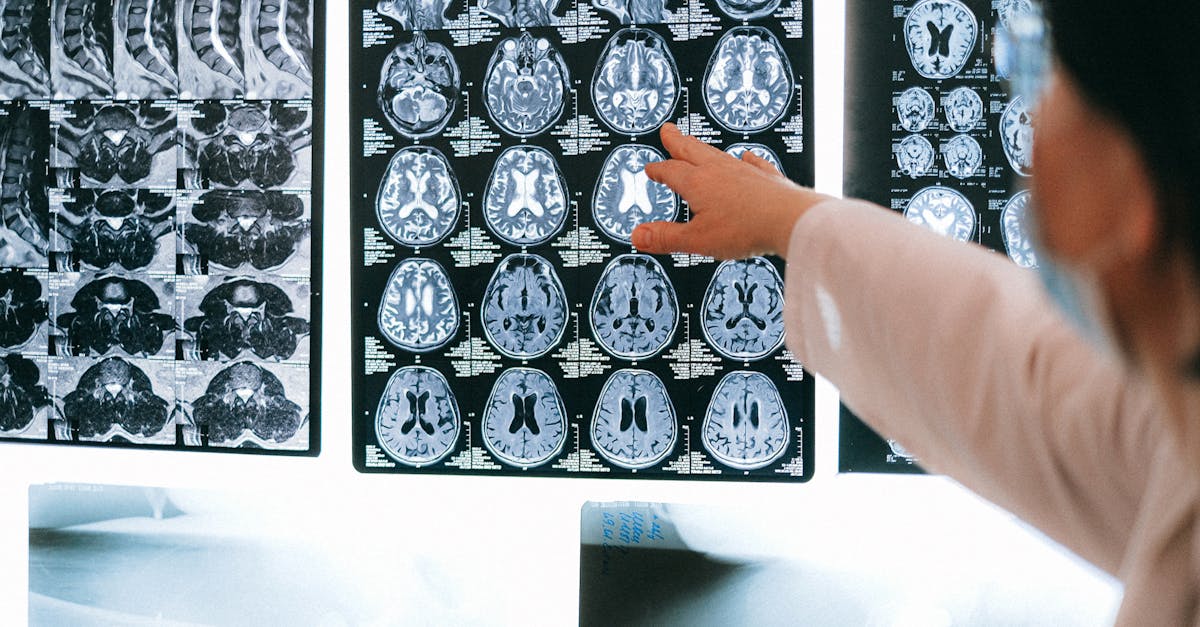
Importance of Neuroimaging
Neuroimaging plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of neurological conditions. It provides clinicians with the ability to visualize structures and functions within the brain, helping to identify abnormalities such as tumors, strokes, and neurodegenerative diseases. Advanced imaging techniques allow for detailed analyses of brain anatomy and activity, aiding in the assessment of functional impairments and facilitating informed treatment decisions.
The insights gained from neuroimaging are invaluable in both research and clinical settings. These techniques not only contribute to understanding the underlying mechanisms of brain disorders but also enhance the effectiveness of therapeutic interventions. As the field of neurology continues to evolve, the integration of cutting-edge neuroimaging modalities into standard practice will likely lead to improved patient outcomes and a deeper understanding of complex neurological phenomena.
Types of Imaging Techniques in Neurology
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in the field of neurology, allowing clinicians and researchers to visualize the brain and nervous system. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is one of the most commonly used methods. It provides detailed images of brain structures and can highlight abnormalities such as tumors or lesions. MRI is favored for its high-resolution capabilities and lack of ionizing radiation, making it a safe choice for patients.
Another significant method is Computed Tomography (CT), which is typically faster and more accessible than MRI. CT scans are particularly useful in emergency situations, as they can quickly identify hemorrhages or strokes. These imaging modalities offer complementary strengths, allowing healthcare providers to select the best approach based on patient needs and specific clinical questions. In addition, advances in functional imaging techniques, such as Functional MRI (fMRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET), enable the assessment of both structure and metabolic activity in the brain, further enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Interdisciplinary Approaches
Neurology often benefits from collaboration with various medical fields, enhancing the understanding of complex neurological conditions. For instance, partnerships with psychiatry can shed light on the relationship between mental health and neurological disorders, allowing for more comprehensive treatment strategies. Similarly, engaging with pharmacology provides insights into how medications impact neural pathways, leading to better clinical outcomes.
Involving other disciplines, such as genetics and immunology, broadens the research landscape. Geneticists can help identify hereditary patterns in neurological disorders, while immunologists can explore how the immune system affects neurological function. This multifaceted approach not only enriches research endeavors but also improves patient care by integrating diverse perspectives and expertise in developing innovative treatment modalities.
Collaborations with Other Medical Fields
Collaboration between neurology and other medical fields enhances patient care and broadens the understanding of neurological conditions. For instance, partnerships with psychiatry enable a more comprehensive approach to conditions like depression and anxiety that often have neurological underpinnings. Integrating insights from neuroscience and psychological treatment can lead to improved therapeutic strategies and better patient outcomes. Additionally, working alongside neurosurgeons facilitates the implementation of advanced surgical techniques for conditions such as epilepsy or brain tumors, ensuring that patients receive the most effective interventions.
Cooperation with disciplines such as radiology is crucial, especially in the realm of neuroimaging. This collaboration allows neurologists to accurately diagnose and monitor cerebral conditions through advanced imaging techniques. Furthermore, partnerships with rehabilitation specialists contribute to developing effective post-treatment care plans, focusing on recovery and quality of life. These interdisciplinary relationships foster innovative solutions and promote a holistic understanding of complex disorders, enriching the field of neurology while ultimately benefiting patients.
FAQS
What foundational subjects should I study to pursue neurology?
To pursue neurology, it's essential to have a strong foundation in biology, chemistry, and physics. Additionally, coursework in psychology and neuroscience can be very beneficial.
How important is research experience for a career in neurology?
Research experience is crucial in neurology as it helps develop critical thinking and analytical skills. It also provides exposure to current methodologies and findings in the field.
What role does neuroimaging play in neurology studies?
Neuroimaging is vital in neurology as it allows for the visualization of brain structures and functions, helping to diagnose conditions, guide treatment, and advance research.
Are interdisciplinary collaborations necessary for studying neurology?
Yes, interdisciplinary collaborations are essential in neurology. They enrich research and practice by integrating insights from fields such as psychiatry, neurosurgery, and rehabilitation.
What types of imaging techniques should I be familiar with for neurology?
It's important to familiarize yourself with various imaging techniques, including MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), CT (Computed Tomography), and PET (Positron Emission Tomography), as each has unique applications in diagnosing neurological conditions.
Related Links
Is MD or DO better for neurology?How many years is neurology training?